Exercise 3 - Connecting a potentiometer
1. INTRODUCTION
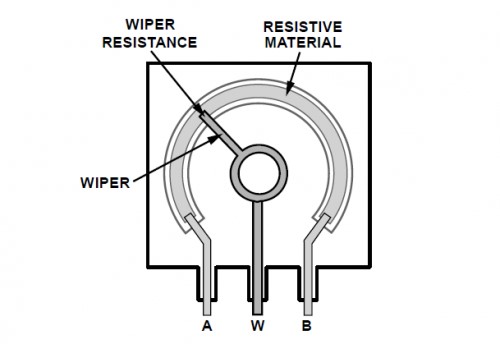
A potentiometer is a three-terminal resistor with a sliding or rotating contact that forms an adjustable voltage divider. If only two terminals are used, one end and the wiper, it acts as a variable resistor or rheostat. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Potentiometer

You can find lineal and logarithmic potentiometers, but for most of programs lineal is extremely recommended.
2. HOW TO CONNECT?
Materials:
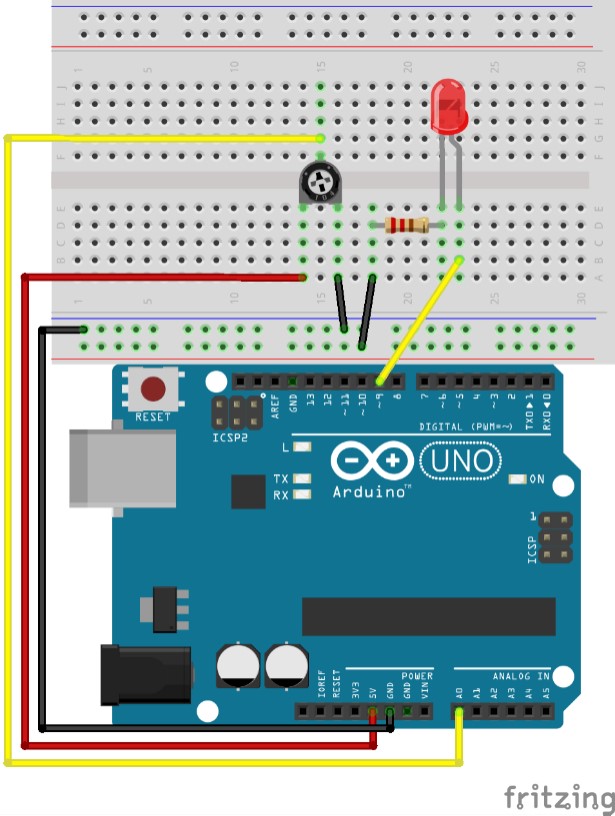
· Arduino UNO board
· Protoboard
· Some wire Jumpers
· Potentiometer
· 220 ohms resistor
· LED
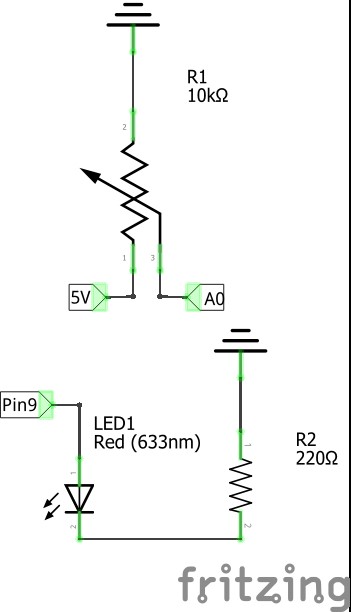
In Arduino you can use a potentiometer as voltage sensor, creating Voltage drop in side terminals (A and B) and connecting wiper (w) to analog pin in Arduino board.
Thus Arduino can read different voltage drops while wiper is rotating.
In next exercises wiper is connected to pin A0 which is set as INPUT in program setup.
|
EXERCISE_A (Potentiometer_and_LED) EXERCISE_B (Changing fading velocity)
|
|
|
3. PROGRAMMING
EXERCISE_A (Potentiometer_and_LED)
This program changes the intensity of a led by a potentiometer. You must define a variable for potentiometer in pin A0 (analog pin) and another one for reading potentiometer value (value). On the other hand,LED pin set in pin9 on Arduino board.
int pot=A0;
int value;
int led=9;//Associate LED to PWM pin
void setup(){pinMode(led,OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
In loop pot value is read by analogRead() and store it in value then the value is written in led using analogWrite().
void loop(){value=analogRead(pot);//read the potentiometer value
value=value/4;//Converts analog read values (0-1023)
//to PWM write values (0-255)
Serial.println(value);
analogWrite(led,value);
}
EXERCISE_B (Changing fading velocity)
This program combines CONNECTING_A_LED_B and USING_SERIAL_PORT_C; it can control the flashing speed with potentiometer while the serial port shows values.
int pot=A0;
int value;
int led=9;//Associate LED to PWM pin
int i=0;
void setup(){pinMode(led,OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
In loop, “i” depends of value through a rule of three, which converts 0-1023 (analog values range) range to 0-8 range in value variable,also you can use the map () function. When the potentiometer rotates “i” equals “i” plus or less converted value.
This means that potentiometer rotation does fade faster or slower.
void loop(){//for increments i , one on one
for(i=0;i<=255;i++){value=analogRead(pot);//read the potentiometer value
analogWrite(led,i);
delay(5);//Delay time is fuction of pot value
i=i+((value*8)/1023);//rule of three to adapt increment value
Serial.print("Pot. value: ");Serial.print(value);
Serial.print(" // Increment of luminosity value: ");Serial.println(i);
}
//for decrements i , one on one
for(i=255;i>=0;i--){value=analogRead(pot);
analogWrite(led,i);
delay(5);
i=i-((value*8)/1023);//rule of three to adapt decrement value
Serial.print("Pot. value: ");Serial.print(value);
Serial.print(" // Increment of luminosity value: ");Serial.println(i);
}
}