Exercise 25 - RFID Communication
1. INTRODUCTION
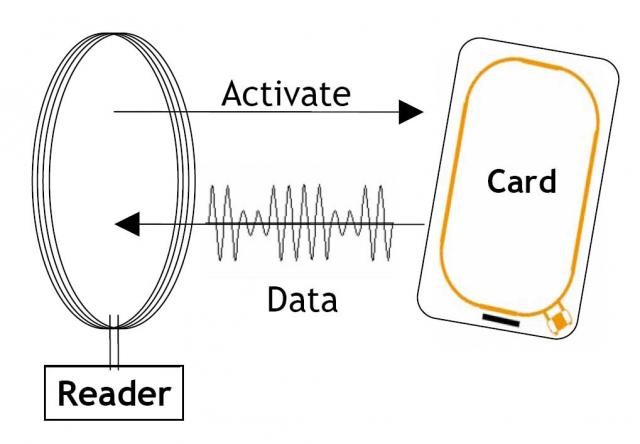
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a wireless system of storing and reading data, which uses devices such as cards, Tags…
There are two types of tags:
· Passive: Not use electrical power source because its circuit is energize by the electromagnetic waves received from the transmitter.
This type of tags not has a long range of communication (1-10cm)
· Active: Use an electrical power source to energize its circuit, increasing range of communication with the transmitter.
2. HOW TO CONNECT?
You can do the connections directly to the board. In this case the device used to RFID communication is RC522 Arduino module. It is energized with 3.3v.
The 3.3Vpin is connected to 3.3V on Arduino and GND to ground on Arduino. You can look the rest of connections on the following table.
|
Materials: ·Arduino UNO board ·Some wire Jumpers ·RFID module |
RC522 |
ARDUINO |
|
3.3v |
3.3v |
|
|
RST |
Pin9 |
|
|
GND |
GND |
|
|
IRQ |
- |
|
|
MISO |
Pin12 |
|
|
MOSI |
Pin11 |
|
|
SCK |
Pin13 |
|
|
SDA |
Pin10 |
|
EXERCISE_A (Turn on a LED)
|
3. PROGRAMMING
To do these exercises you have to install RC522_RFID-master library.
EXERCISE_A (READING CARDS)
#include <SPI.h>
#include <MFRC522.h>
#define RST_PIN 9 //Pin 9 to do reset on RC522
#define SS_PIN 10 //Pin 10 (SDA) of RC522
MFRC522 mfrc522(SS_PIN, RST_PIN); //Create the object of RC522
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); //Initialize Serial communication
SPI.begin(); //Initialize SPI bus
mfrc522.PCD_Init(); // initialize created object MFRC522
Serial.println("UID reading");
}
void loop() {
//Check if exist new cards. Condition is acomplised if
// it is true
if ( mfrc522.PICC_IsNewCardPresent())
{
//Select card
if ( mfrc522.PICC_ReadCardSerial())
{
// Send UID via Serial
Serial.print("Card UID:");
//This for loop is used to join UID terms and then print them.
for (byte i = 0; i < mfrc522.uid.size; i++) {
//(relational expresion) ? (expresion1) : (expresion2)
//It is the same than a if condition
Serial.print(mfrc522.uid.uidByte[i] < 0x10 ? " 0" : " ");
Serial.print(mfrc522.uid.uidByte[i], HEX);
}
Serial.println();
// Finish the reading
mfrc522.PICC_HaltA();
}
}
}
EXERCISE_B (AUTHENTICATION)
//Code based on http://www.naylampmechatronics.com/blog/22_Tutorial-Lector-RFID-RC522.html
#include <SPI.h>
#include <MFRC522.h>
#define RST_PIN 9 //Pin 9 to do reset on RC522
#define SS_PIN 10 //Pin 10 (SDA) of RC522
MFRC522 mfrc522(SS_PIN, RST_PIN); //Create the object of RC522
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); //Initialize Serial communication
SPI.begin(); //Initialize SPI bus
mfrc522.PCD_Init(); // initialize created object MFRC522
Serial.println("Access control: ");
}
byte CurrentUID[4]; //Store the code of read tag
byte User1[4] = {0xC5, 0xF6, 0x37, 0xD5} ; //code of user 1
byte User2[4] = {0xE6, 0x88, 0x44, 0x49} ; //code of user 2
void loop() {
//Check if exist new cards. Condition is acomplised if
// it is true
if ( mfrc522.PICC_IsNewCardPresent())
{
//Select card
if ( mfrc522.PICC_ReadCardSerial())
{
// Send UID via Serial
Serial.print(F("Card UID:"));
//This for loop is used to join UID terms and then print them.
for (byte i = 0; i < mfrc522.uid.size; i++) {
//(relational expresion) ? (expresion1) : (expresion2)
//It is the same than a if condition
Serial.print(mfrc522.uid.uidByte[i] < 0x10 ? " 0" : " ");
Serial.print(mfrc522.uid.uidByte[i], HEX);
CurrentUID[i] = mfrc522.uid.uidByte[i];
}
Serial.print(" ");
//Compare the UIDs to determine if it is the UID of a user
if (compareArray(CurrentUID, User1) || compareArray(CurrentUID, User2))
Serial.println("Access granted...");
else
Serial.println("Access denied...");
// Finish the reading
mfrc522.PICC_HaltA();
}
}
}
//Function to compare two vectors
boolean compareArray(byte array1[], byte array2[])
{
if (array1[0] != array2[0])return (false);
if (array1[1] != array2[1])return (false);
if (array1[2] != array2[2])return (false);
if (array1[3] != array2[3])return (false);
return (true);
}

