Exercise 4 - Using serial port
1. INTRODUCTION
In Arduino, serial communication is used many times to receive/transfer data to PC or another Arduino.
When serial communication is being used pin0 and pin1 aren’t available.
Serial communication in Arduino is asynchronous; this means that data can be transmitted intermittently rather than in a steady stream.
2. HOW TO CONNECT?
Materials:
· Arduino UNO board
· Protoboard
· Some wire Jumpers
· Potentiometer
· 220 ohms resistor
You can use Rx and Tx pin or connect Arduino to PC by wire. You can use typical functions to use serial communication in Arduino.
· begin()
· end()
· read()
· print()
· println()
All of this function is called by Serial.”function”.
To use serial communication in this exercise its necessary recover CONNECTING_A_LED_A, CONNECTING_A_LED_B, CONNECTING_A_POTENTIOMETER_A. The connections are identical.|
EXERCISE_A (Serial with potentiometer) |
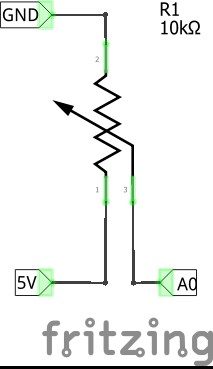
|
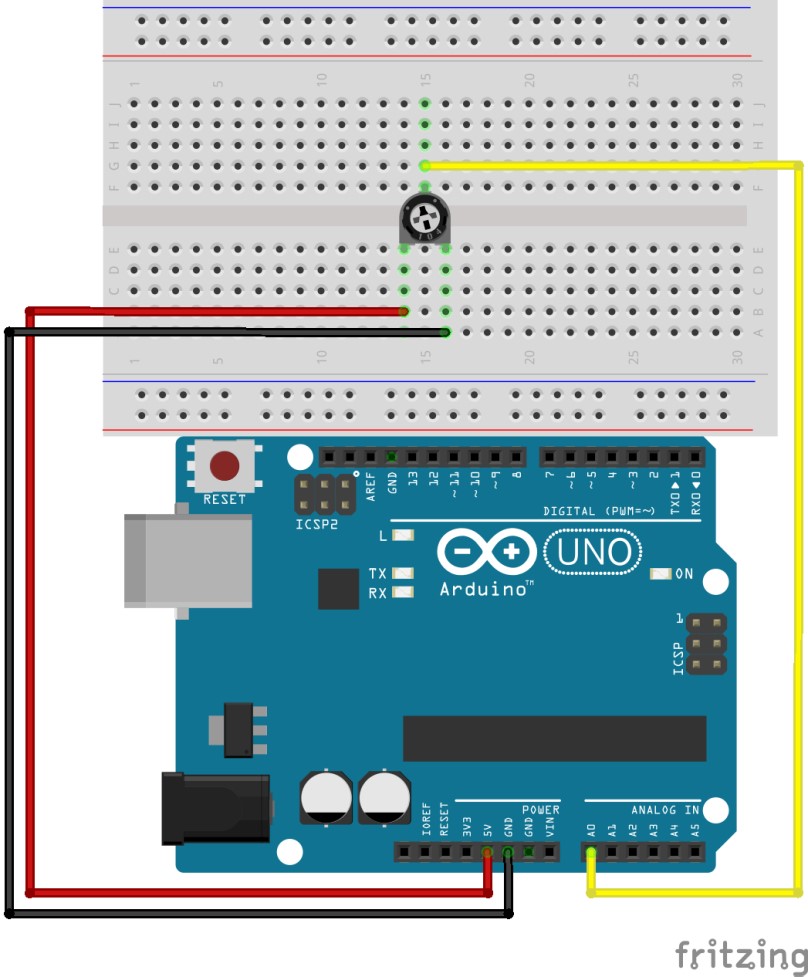
|
|
EXERCISE_B (Visualize fade values) |

|

|
|
EXERCISE_C (Turn on and of LED with a serial command |
|

|
3. PROGRAMMING
EXERCISE_A
This program shows on serial monitor analog values read in potentiometer.
In setup serial is initialized at 9600 bauds (data transfer velocity) and potentiometer pin set as INPUT).
int pot=A0;
int lectura;
void setup(){
pinMode(pot,INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
In loop read pot values and save it in lectura by analogRead(), then lectura is printed by Serial.println() which prints and introduces carriage return.
void loop(){
lectura=analogRead(pot);
Serial.println(lectura);
}
EXERCISE_B
This program is similar to the previous. In this case serial communication shows how fade value changes.
int led=9;//Associate LED to PWM pin
int i=0;
void setup(){
pinMode(led,OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);//Initialize serial communication at
// 9600 bauds
}
Loop writes increasing and decreasing “i” value in LED and prints it in serial monitor.
void loop(){
//for increments i one on one each 5 miliseconds
for(i=0;i<=255;i++){
analogWrite(led,i);
delay(20);
Serial.println(i);//Prints i value
}
//for derements i one on one each 5 miliseconds
for(i=255;i>=0;i--){
analogWrite(led,i);
delay(20);
Serial.println(i);//Prints i value
}
}
EXERCISE_C
Serial communication is not used only to print something in serial monitor also you can send information through it. In this program, option is a variable, which store a character.
int led=13;//Assign the name led to pin 13
int option;
void setup(){
pinMode(led,OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);//Start serial communiation at 9600 bauds
}
In loop Serial is read (to use correctly this program you should send one character by serial monitor).
If option value is ‘a’ Arduino writes HIGH level in led and prints “ON” in serial monitor. On the other hand if value is ‘b’ Arduino writes LOW level in led and prints “OFF”.
void loop(){
//if Serial is available
if(Serial.available()>0){
option=Serial.read();//Serial port is read
if(option=='a'){// if option is caracter "a" led turn on
digitalWrite(led,HIGH);
Serial.println("ON");
}
if(option=='b'){ // if option is caracter "off" led turn off
digitalWrite(led,LOW);
Serial.println("OFF");
}
}
}

